

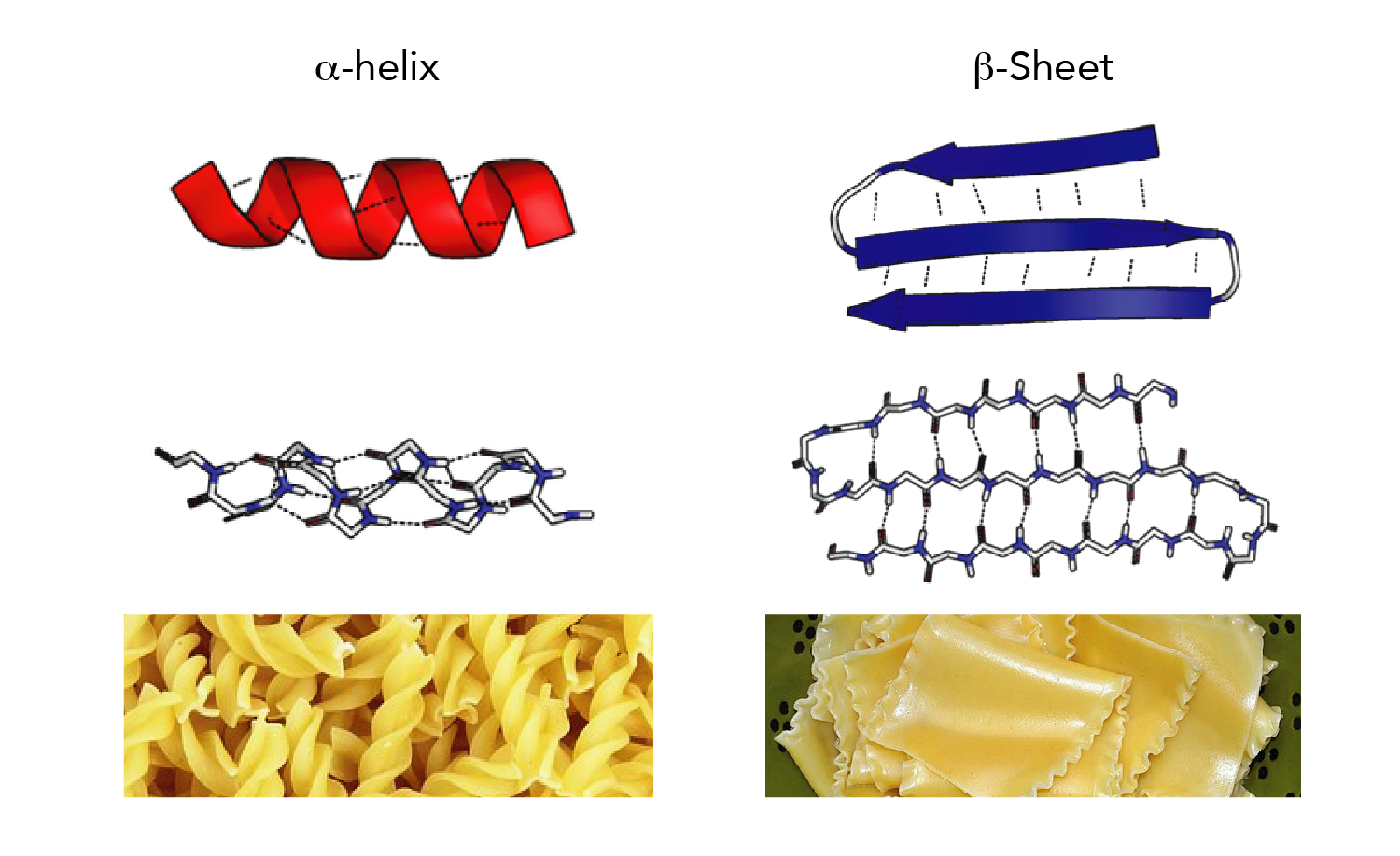
Consequently H-bonds are between adjacent strands and perpendicular to the direction of the strand. Two or more beta-strands make a beta-sheet. Due to the extended nature of the polypeptide it is not possible to form mainchain hydrogen bonds between adjacent residues.
Consequently, beta structures consist of straight, fully extended, strands of linked amino acids which are called beta-strands. These particular phi and psi torsional angles generate a building block that is almost a perfect rectangular prism. In all cases each peptide bond is rigid and planar in the trans conformation. In all cases these secondary structures of proteins have characteristic values of the \(\Psi\) and \(\Phi\) torsional angles that are the same for each residue within a particular secondary structure. Minimizing steric clashes of mainchain and sidechain atoms.Maximize van der Waals interactions of mainchain atoms.These conformations are stable because they: A left-handed alpha helix is also stable, but relatively rare. Only two are commonly observed in proteins, the right-handed alpha helix and beta-structures. Given the possible values of \(\Phi\) and \(\Psi\) angles, many different shapes of the amino acid building block are possible and therefore many different three dimensional structures are possible.
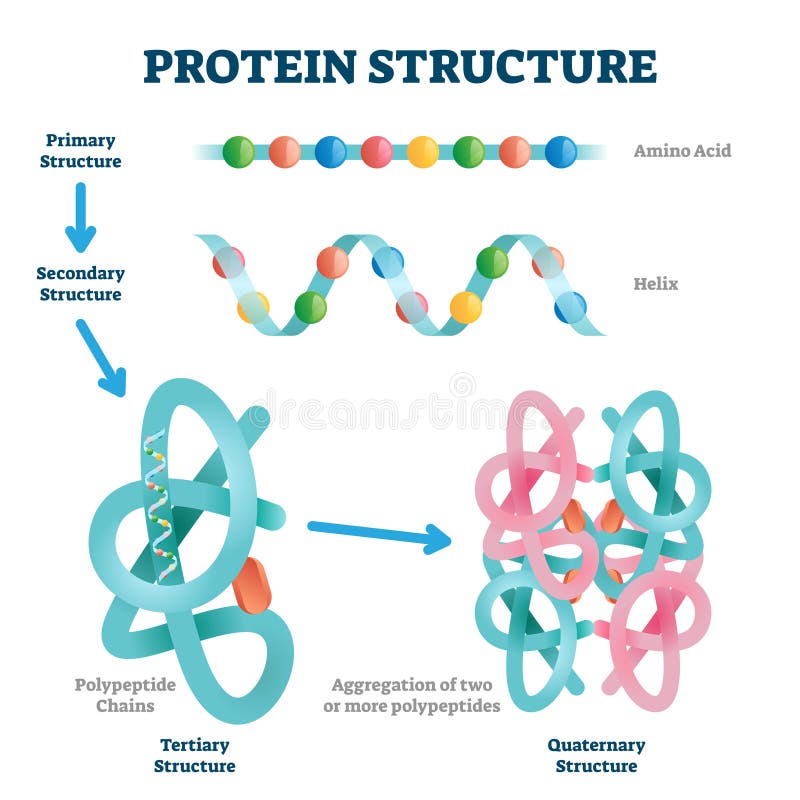
If the building block is a perfect rectangular prism, then the structure will remain linear. In the case of three dimensional building blocks that have some degree of curvature on both faces, the two dimensional circular structure becomes a helix. The radius of the circle is related to the degree of curvature. A straight chain occurs if the is no curvature in the block, while a circle will result if there is any degree of curvature. In two dimensions there are two possibilities, either a straight chain or some type of circle (which may or may not be closed). If a series of identically shaped objects are laid end-to-end they will form some type of geometrical structure. In regular secondary structures these angles are the same for each residue, and thus the shape of each building block, or amino acid, is the same. The shape of each block depends on the \(\Phi\) and \(\Psi\) angle of each residue. Proteins consist of a linear chain of amino acids, with each amino acid representing a build block.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
